MOS tube (field effect transistor) amplifier circuit and principle
The field-effect transistor (FET) amplifier is a voltage-controlled device that boasts high input impedance and low noise, making it a popular choice for electronic circuits, especially in preamplifiers. Junction field-effect transistors (JFETs) and insulated-gate field-effect transistors (IGFETs/MOSFETs) can both form corresponding FET amplifiers. Below is an example of the equivalent circuits and performance index calculation expressions for the three basic configurations of amplifiers, as detailed in Table 5.2-7. The image demonstrates that FETs exhibit a positive control effect similar to transistors, enabling them to create three fundamental amplifier configurations: common source, common drain, and common gate.
1. Bias Circuit: Different types of FETs operate in the amplification region under varying conditions, requiring distinct polarities for the gate voltage. For instance, JFETs require the gate-source and drain-source voltages to have opposite polarities, whereas MOSFETs need these voltages to share the same polarity. Depletion-mode MOSFETs can be positively biased, zero-biased, or negatively biased depending on the application.
Based on these characteristics, there are two primary types of bias circuits for single-supply configurations: (1) Self-bias circuit, which is self-biasing for JFET and depletion-mode MOSFET amplifiers. Figure 5.2-6 illustrates an N-channel JFET self-biasing circuit. The gate-source voltage is UGS = RID. (2) Hybrid bias circuit, suitable for various FET amplifiers. Figure 5.2-7 shows the hybrid bias circuit for an N-channel enhancement-mode MOSFET amplifier.
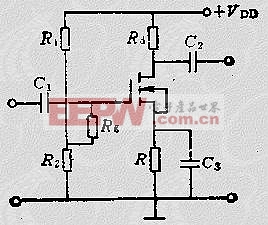
Figure 5.2-7 Hybrid Bias Circuit
2. Equivalent Circuit and Performance Index Calculation Formula for Field-Effect Transistor Three Basic Configurations (as per Table 5.2-7)
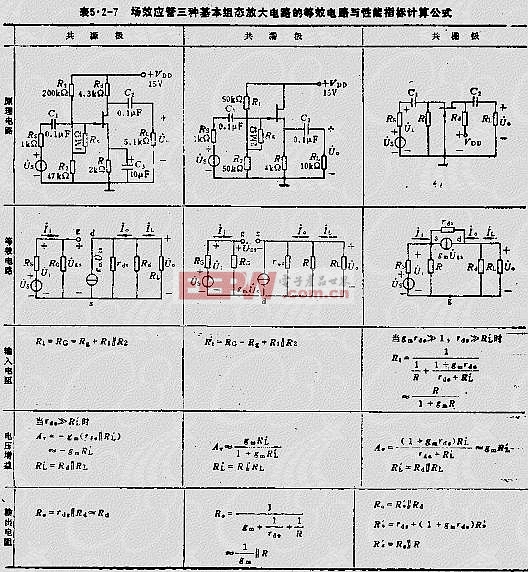
Gate-source voltage:
In practical applications, the design and implementation of FET amplifiers demand careful attention to detail. The biasing network plays a critical role in ensuring optimal performance by setting the operating point correctly. For instance, the self-bias circuit provides a straightforward method for achieving stable operation, while the hybrid bias circuit offers more flexibility in complex designs. Additionally, understanding the intrinsic properties of different FET types helps engineers select the most appropriate device for their specific needs.
From audio equipment to RF systems, FET amplifiers are indispensable components due to their excellent linearity and low distortion characteristics. Engineers must also consider factors such as thermal management and power efficiency when designing circuits involving FETs. Proper layout techniques and component selection contribute significantly to the overall reliability and performance of the final product.
Moreover, advancements in semiconductor technology continue to enhance FET performance, offering new opportunities for innovation in electronics. By leveraging the unique features of FETs, designers can create cutting-edge solutions tailored to meet modern demands. Whether it's improving signal integrity or reducing power consumption, FET amplifiers remain at the forefront of technological progress.
1.2 Inch Fnd Numeric Display,Indoor Fnd Numeric Display,Single Digit Fnd Numeric Display,1 Digit Fnd Numeric Display
Wuxi Ark Technology Electronic Co.,Ltd. , https://www.arkledcn.com