Sprite mobile video surveillance system based on J2ME
1 Introduction
With the development of society, video surveillance technology has been widely used in all walks of life. How to allow users to monitor anytime and anywhere, mobile phone mobile monitoring system provides a good solution. Through the combination of wireless network and Internet, the mobile phone mobile monitoring system transmits the video signal of the monitoring equipment through the mobile internet to realize real-time online monitoring of the scene. At present, the technology adopted by mobile phone mobile monitoring systems mainly uses J2ME's P layer player technology for on-site monitoring. Not only does the mobile phone need to support real-time streaming media protocols such as RTSP, but also has certain requirements for mobile Internet. This article uses Sprite of J2ME to display the live monitoring pictures transmitted by the server with the effect of animation, to simulate video monitoring, and to meet the requirements of real-time video monitoring.
2 System design
The mobile monitoring system for mobile phones is composed of four main parts: video collector, server, mobile Internet and mobile phone. The overall architecture is shown in Figure 1.
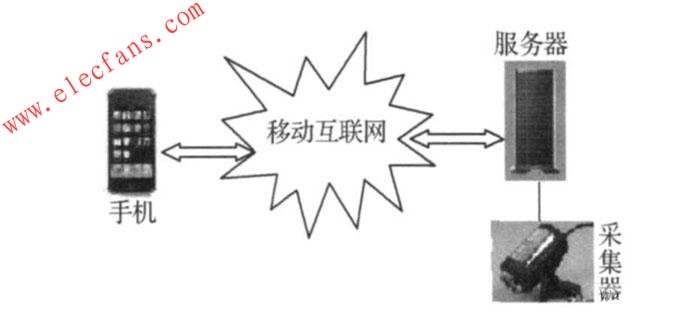
Figure 1 Overall architecture diagram
System functions: 1) Video image collection and encoding, store the image acquired by the video collector on the server in an appropriate encoding format; 2) Image transmission, when the user sends a request to the server, the server sends the collected image according to the request To the user's mobile phone terminal, the transmission uses the Datagram method; 3) The display of the image, after the mobile phone terminal obtains the image, if it is non-abnormal, the image is displayed in a static manner, if it is abnormal, the mobile terminal is displayed in the form of animation Image and video; 4) Other auxiliary functions, such as abnormal alarm, access permission setting, video capture, monitoring equipment control and other functions.
System work flow: The video collector collects and transmits the on-site situation to the server. After the server receives the collected data, it processes the data and saves it in the database in time. At the same time, it waits for the mobile phone to connect and access. The collected on-site situation is transmitted to the mobile phone terminal through the mobile Internet, so that the user can monitor the on-site situation. Considering the actual network traffic and other issues, and the scene (the user's home or office) is not abnormal, it is in the same state, so the monitoring system only needs to send a scene key frame picture to the user's mobile phone, only when the scene is abnormal , The monitoring system will warn the user, and then according to the user's requirements, the scene will be continuously sent to the user's mobile phone in the form of key frame pictures. The user's mobile phone will display the live pictures to the user in the form of animation effects through J2ME Sprite Real-time video surveillance on site, and save network traffic.
Server-side design: The server-side runs on a remote computer and is implemented by J2SE. Its main function is to capture and save on-site monitoring data. The specific steps are as follows: 1) Obtain the address of the video collector; 2) Enter the video sequence collected by the video collector into the data pool; 3) The server uses an appropriate key frame algorithm to extract the corresponding key frame from the video sequence ; 4) According to the client's request to send the corresponding key frame picture data.
Design of the client: The main function of the client is to display the live monitoring pictures transmitted by the server through the animation effect, simulate the video playback, and realize the real-time video monitoring on the spot. Its hardware requirements:
As a monitoring mobile phone, there are no special requirements in this system, only need to support M IDP 2.0 (currently mobile phones have generally supported M IDP 2.0).
3 Implementation of the system
3. 1 server-side implementation
The system server platform uses Apache Tom ca, t. For server-side implementation, this article mainly discusses how to perform server-side network connection and image data transmission. The codes involved are Server. Java and Sender. Java. Server. Java is used to establish a server-side connection, accept the client's request, obtain the client's address based on the client's datagram, and then transmit the processed field information from the collector to the user in the form of a picture by SSender. Java Mobile terminal.


3. 2 client implementation
Mobile phone terminals are mainly related to technologies such as user interface programming, client communication, and monitoring image display in J2ME. MONitor. Java code is used to depict the user interface; Clien.t java code establishes the client communication connection, accepts the server-side picture data and displays; CSender. Java code is similar to the server-side SSender. The java code is mainly used for the transmission of client information.
public class C lienTImplements Runnable
{

;


Figure 2 Test chart.
4 Experiment
According to the above design and implementation, this article uses Tom cat6.0, J2MEW ire lesSToo lk it2.5 as the experimental platform to test the system, the test results are shown in Figure 2. These three pictures were captured at different moments when the mobile phone played an animation to monitor the scene. The results of the system test meet the requirements of real-time video surveillance.
5 Conclusion
The innovation of the mobile video surveillance system solution proposed in this article is: the use of Sprite technology to display on-site monitoring in the form of animation effects, which meets the requirements of real-time video surveillance and avoids the current use of mobile phone players to play real-time video. A series of questions, at the same time, combine the animation form with the static picture form, saving network traffic. This solution is simple to implement, is not subject to the restrictions of mobile phone model and technology (only requires the mobile phone to support M IDP 2.0), and has wide applicability.
1.The heat transfer rate is up to more than 90%, saving energy and
electricity
2. The honeycomb circuit has planar heating, and the effective
heating area accounts for a large proportion, about 60% of the
product area, and the heated object is heated more evenly
3. Radiate far-infrared light wave, making the heat source softer
4. Wide circuit and connected design, no need to worry about
crimping the circuit break
5. Add the thermostat protection device, which can ensure the
product safety under bad conditions and effectively prevent the
superhigh temperature of the object being heated
Under Tank Pad,Greenhouse Heater for Plant Growing,Electric Seeding Mat,Germinate Seeds Heating Pad
ShenZhen XingHongChang Electric CO., LTD. , https://www.xhc-heater.com