What is the secret of insulation design in switching power supplies?
The current flowing through the human body causes a physiological reaction of the human body. The intensity of the reaction depends on the magnitude of the current, the duration, and the path through the human body. Generally, only 0.5mA current is needed, which can affect healthy human body and may cause indirect harm. Larger currents can cause direct damage to the body, such as burns or fibrillation in the ventricles.
In general, in the case of drying, a voltage of less than 40V peak or 60V DC is generally considered to be a non-hazardous voltage. However, exposed parts that must be touched during use or that require manual operation should be protected or properly disposed of.
In order to prevent the human body (operator or maintenance personnel) from being shocked, it is necessary to comply with relevant industry safety design standards such as IEC60950, GB G4943 in the design of switching power supply; in these standards, the different positions of the switching power supply are insulated. Requirements to ensure the safety of the operator.
Insulation categoryFunctional insulation (FuncTIonal InsulaTIon): The purpose of functional insulation is to maintain the product's normal operation and does not have any safety functions. Such insulation is typically used between two conductors in the same line, ie, parts that do not have safety isolation requirements. For example, the green oil on the PWB, the plastic casing of the electrolytic capacitor is functional insulation.
Basic InsulaTIon: The purpose of basic insulation is to provide a basic protection against electric shock to avoid the risk of electric shock. However, such insulation can only guarantee safety under normal conditions, but it cannot guarantee the safety of transient voltage. In other words, when transient voltages occur, the basic insulation may collapse.
Supplementary Insula TIon: In addition to the basic insulation, additional insulation is provided to provide another layer of insulation when the primary insulation fails. In general, the requirements for supplemental insulation are the same as the basic insulation, so the roles between the two are interchangeable. For example, a cable has two layers of insulation. We can say that the inner layer is the basic insulation and the outer layer is the supplementary insulation. On the other hand, it is also possible.
We must pay attention to the fact that supplemental insulation must be established in the presence of basic insulation.
Double Insulation: This refers to insulation that includes both basic and supplementary insulation. This insulation provides adequate safety and protection against electric shock as long as the location is correct.
Reinforce Insulation: It provides the same degree of insulation as double insulation, but it differs from double insulation in that it is not easily divided into basic insulation and supplementary insulation. It may be an integrally formed spacer, or Insulation consisting of many spacers.
Clearance and creepage distanceClearance: The shortest spatial distance measured between two conductive parts or between the conductive parts and the equipment interface. The measurement of this distance does not limit the way in which it is used. For example, if a product uses an insulating material as the outer casing, the opening or the gap of the outer casing should be considered as a conductor. Just as a layer of aluminum foil is laid on it, it must still be kept at a certain distance from the internal dangerous parts, because these places are A place that is easily accessible to users.
Creepage distance: refers to the shortest distance between two conductive parts measured between the two conductive parts or between the conductive parts and the protective interface of the equipment. In general, if the pollution level is not 1, the creepage distance is usually greater than the clearance.
Clearance and creepage distance are related to working voltage, pollution level, altitude, and insulation materials. The actual design clearance and creepage distance requirements on the PCB shall be calculated according to the requirements of the insulation level, working voltage, pollution level, altitude, and insulation materials.
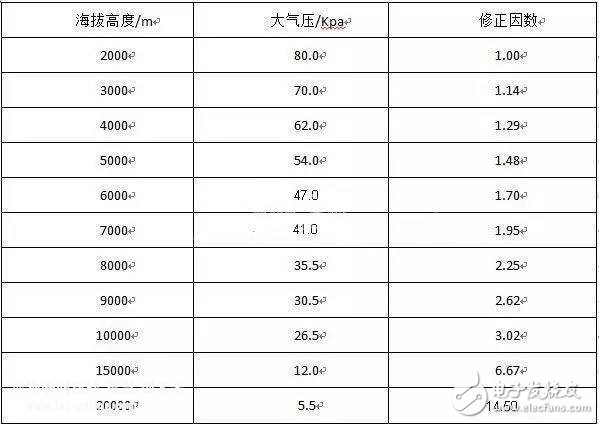
Altitude: According to Bass's law, the breakdown voltage of a harmonious electric field is proportional to the product of the air pressure and the distance between the two poles. When the distance between the two poles is constant, the lower the air pressure, the lower the breakdown voltage. The air pressure is inversely proportional to the altitude, so altitude is one of the important factors affecting the spatial distance.
The general safety standard sets the maximum altitude of the product to 2000M. If it exceeds 2000M, a correction factor needs to be considered, as shown in the following table:
Pollution degree: If the space between the two conductors has pollutants, it will also affect the degree of insulation. The general standard divides pollution into four levels:
Pollution Degree 1: No contaminants or only dry and non-conductive contaminants. You can use a closed casing or apply the surface of the board to meet this level of pollution.
Pollution Degree 2: Refers to the contamination of occasional conductive contaminants, such as condensation of water vapor. Generally there is only non-conductive pollution, but occasional transient conductive pollution due to condensation must be considered.
Pollution Degree 3: Conductive contamination, or non-conductive pollution becomes conductive due to expected condensation.
Pollution Degree 4: Causes persistent conductive pollution, such as pollution caused by conductive dust or rain and snow. Unless otherwise specified in the relevant product standards, industrial electrical appliances are generally selected for use in pollution level 3 environments, and household and similar electrical appliances are generally selected to have a pollution level of 2 levels.
For the primary circuit and the clearance requirements between the primary circuit and the secondary circuit, IEC60950-2001 is specified as such.
Floor heating pipe refers to a pipe used as a circulating flow carrier of low temperature hot water in the ground radiation heating system of low temperature hot water.
Floor heating pipe refers to a pipe used as a circulating flow carrier of low temperature hot water in the ground radiation heating system of low temperature hot water.
According to the production mode, crosslinked polyethylene is divided into four types: peroxide crosslinking (PE-XA), silane crosslinking (PE-XB), electron beam crosslinking (PE-XC) and azo crosslinking (PE-XD).
Among them, peroxide crosslinking and silane crosslinking are two commonly used crosslinking polyethylene pipe products in China.
Pex Cross Linked Polyethylene has no chemical crosslinking agent and catalyst added in the crosslinking process, and no harmful low-molecular compounds, so it will not pollute the liquid delivered. It is a new generation of healthy and environmentally friendly Crosslinked PE Pipe.Can be used as Heat Pipe and widely used in high-end, precision,HVAC and Water Supply System at High Temperature and High Pressure.
We are the professional manufacturer of Electrical Tapes,Insulating Tape and Cross Linked Polyethylene Water Pipe in China for more than 25 years,if you want to know more information about our company and products, please visit our website.
Heat Pipe,Heat Tube,Heat Shrinkable Pipe,Heat Shrink Tubing Electrical
CAS Applied Chemistry Materials Co.,Ltd. , https://www.casac1997.com