Introduction to the design of piezoelectric wafer keyboard
Are you still worried that your keyboard is "fear of water"? The piezoelectric disc keyboard is here to solve all your concerns. This innovative design uses a piezoelectric disc as both a sensor and a buzzer, detecting even the slightest pressure on a 0.4mm-thick stainless steel plate. It’s not only waterproof but also highly resistant to vandalism. In this article, we’ll walk you through the design of this unique piezoelectric wafer keyboard.
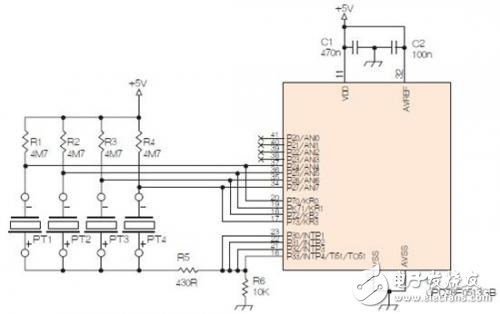
At the heart of the sensor is a piezoelectric disc, commonly used as a buzzer. For this project, we’ve chosen Murata’s 7BB-35-3 model, which has an outer diameter of 35mm and a sensing area of about 20mm. The PCB features electronic components and round holes that allow the ceramic material to move freely. To secure the disc in place, a 3mm thick self-adhesive foam rubber is used, and the assembly is clamped to the back of the front panel with appropriate pressure.
Below is the PCB layout and opening for reference:
Car Phone Wireless Charging Coil,Circuit Board Induction Coils,Intersection Induction Coils,Induction Coil Set
Shenzhen Sichuangge Magneto-electric Co. , Ltd , https://www.scginductor.com